Structure of the private distribution network
Generally, with an HV power supply, a private distribution network comprises (see Figure 1-1):
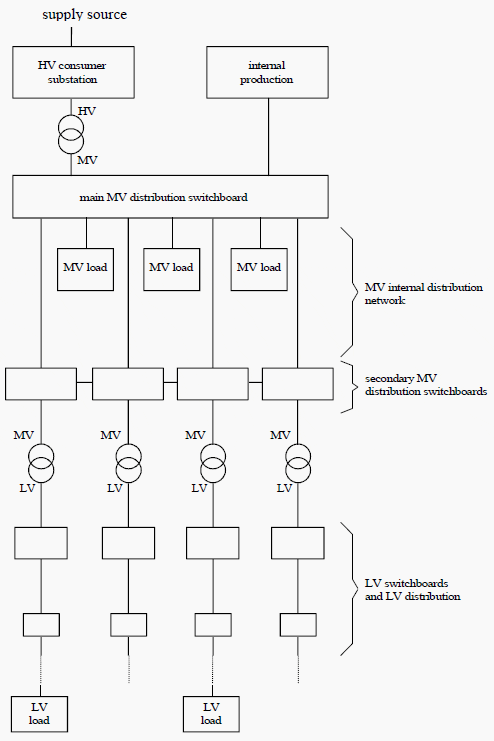
- An HV consumer substation fed by one or more sources and made up of one or more busbars and circuit-breakers;
- An internal generation source;
- One or more HV/MV transformers;
- A main MV switchboard made up of one or more busbars;
- An internal MV network feeding secondary switchboards or MV/LV substations;
- MV loads;
- MV/LV transformers;
- Low voltage switchboards and networks;
- Low voltage loads.
The supply source
The power supply of industrial networks can be LV, MV or HV. The voltage rating of the supply source depends on the consumer supply power. The greater the power required, the higher the voltage must be.
HV consumer substations
The most usual supply arrangements adopted in HV consumer substations are: Single power supply.
Advantage: – reduced cost.
Disadvantage: – low reliability.
Disadvantage: – low reliability.
Note: The isolators associated with the HV circuit-breakers have not been shown.



ello,
ReplyDeleteNice! Post.
Thank you for sharing.
share more about Electrical Networks